With the development of 5G/10G and Ultra High Definition Video, the demands for over 1GbE network interface are increasing. Although 10GbE has existed, it requires advanced technology and higher cost. At the moment, 2.5GbE which is between 1GbE and 10GbE is created. More and more devices support a 2.5GbE port. Besides, many laptops no longer provide Ethernet ports so people should use USB to RJ45 to have a 2.5GbE LAN port. Then, what is 2.5GbE exactly and what features can it bring? Below we will explain. Before that, let’s get to know what Multi-Gig is first!

Part I. What is Multi-Gig?
Multi-Gig refers to the Ethernet speed from 1Gbps to 10Gbps. The previous Gigabit Ethernet and 10G Gigabit Ethernet don’t support speeds between 1Gbps and 10Gbps. They separately only support 1Gbps and 10Gbps. Therefore, devices that support Multi-Gig such as NAS, switch, and Multi-Gig ONU can’t bear to run when they connect to a Multi-Gigabit Ethernet port. The Multi-Gig Ethernet port supports 100Mbps, 1Gbps, 2.5Gbps, and 5Gbps.
Part II. What is 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet (2.5GbE)?
Like Multi-Gig, 2.5 Gigabit Ethernet(2.5GbE) supports speeds between 1GB and 10GGB, contributing to making your devices run at full rates without other settings. 2.5GbE supports 10Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps, and 2.5Gbps. Upgrading from 1GbE to 2.5GbE means the network speed is improved, which is 2.5 times faster than Gigabit Ethernet and achieves the previous infeasible possibility of the network. The latency is extremely low. Therefore, with 2.5GbE, users can acquire better Internet service whether in E-sport games, live streams, or office downloads.
Part II. 1GbE vs 2.5GbE vs 10GbE, what’s the difference?
✔ 1GbE
Gigabit Ethernet is a version of the Ethernet technology broadly used in local area networks (LANs) for transmitting Ethernet frames at 1 Gbps. It’s used to describe various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of gigabits per second, as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2005 standard. The standard allows for half-duplex gigabit connections via hub connections, but the speeds achieved on the market with full-duplex connections using switches are truly standard. Gigabit Ethernet is a technology built on top of the underlying Ethernet standard.
✔ 10GbE
10 Gigabit Ethernet (10 GbE) is a telecommunication technology that offers data speeds up to 10 billion bits per second. It’s originally adopted in 2002 as IEEE Std 802.3ae-2002. 10GE also retains the Ethernet minimum and maximum frame length specified in the 802.3 standard. This enables users to communicate with lower-speed Ethernets conveniently when upgrading their existing Ethernets. Due to the high data rate, 10GE no longer uses copper wire but only uses optical fiber as the transmission medium. It uses long-distance optical transceivers and single-mode fiber interfaces to work in wide area networks and metropolitan area networks. 10GE can also use cheaper multimode fiber, but the transmission distance is 65~300m.
✔ 2.5GbE
The market for 2.5GbE is enlarging and more and more 2.3GbE routers are producing and selling. Therefore, compared with 10GbE, the cost of 2.5GbE devices and deployment is relatively lower. One of the factors that accelerates the development of 2.5GbE is WiFi 6 which enables wireless connection to over 1GbE LAN. Recently, some new WiFi 6 solutions include 2.5GbE ports or even 10GbE ports. In addition, upgrading to 2.5GbE is worthy especially for small enterprises because of its availability and cost-efficiency. There is no need for rewiring and the current CAT5e can be used in your present Ethernet connection.
Nowadays, more and more devices are providing Multi-Gig/2.5G Ethernet ports. Below we take an example with V-SOL ONU V2902RH that provides a 2.5GbE port.
Part III. Related 2.5GbE Product: V-SOL V2802RH
V-SOL product V2802RH takes a 2.5GbE LAN port and supports dual modes of xPON including EPON and GPON. The 2.5GbE port fits the latest computers/laptops and performs GPON well without any latency. In addition, the 2.5GbE router is small and flexible, making wifi signal cover around the house. It can be used in games, family networks, SOHO, business, etc.
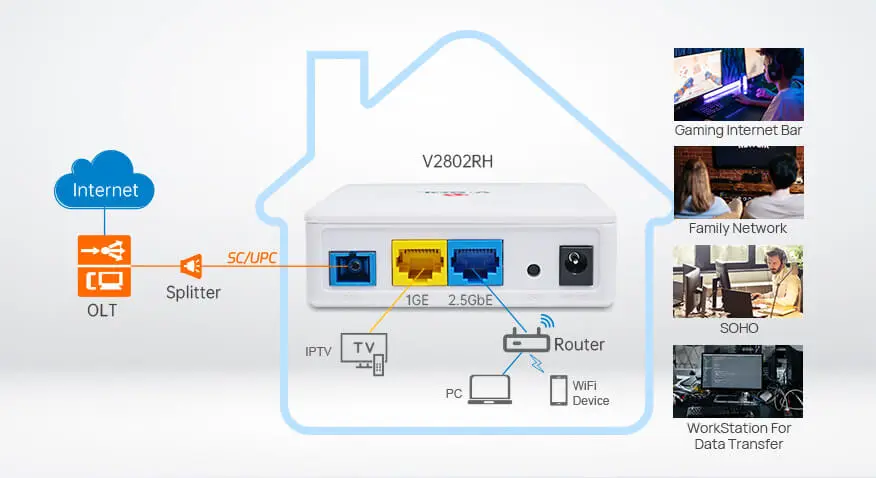
What should be noticed is that only when the device that connects to the ONU supports 2.5GbE, then the real speed is possible to reach up to 2.5GbE theoretically. If the router, mobile phone or computer doesn’t support 2.5GbE, then your devices only can reach 1GbE. 2.5GbE is a theoretical value and the real speed can’t reach it. Even in the application of enterprise switch with 2.5GbE, the speed will be distributed to different ports and the speed of each port should be less than 2.5GbE.